What Is a Statement of Retained Earnings? What It Includes
An investor may be more interested in seeing larger dividends instead of retained earnings increases every year. They need to know how much return they’re getting on their investment. The statement of retained earnings paints a clear picture of that. Different companies how to handle discounts in accounting chron com have different strategies regarding their dividends. A company that routinely gives dividends to shareholders will tend to have lower retained earnings, and vice versa. To better explain the retained earnings calculation, we’ll use a realistic retained earnings example.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Assumptions
Shareholders and management might not see opportunities in the market that can give them high returns. For that reason, they may decide to make stock or cash dividend payments. Retained earnings result from accumulated profits and the given reporting year. Meanwhile, net profit represents the money the company gained in the specific reporting period. 11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas.
What does the statement of retained earnings include?
This information will be listed on the balance sheet under the heading “Retained Earnings.” Between 1995 and 2012, Apple didn’t pay any dividends to its investors, and its retention ratio was 100%. But it still keeps a good portion of its earnings to reinvest back into product development.
Growth Potential
Paying the dividends in cash causes cash outflow, which we note in the accounts and books as net reductions. They want to know about the returns generated by retained earnings. And they want to know whether they can do better with other investments.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
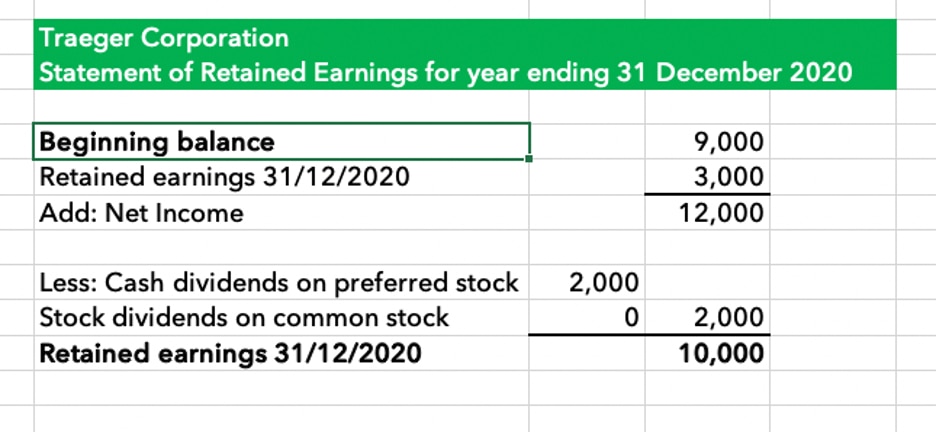
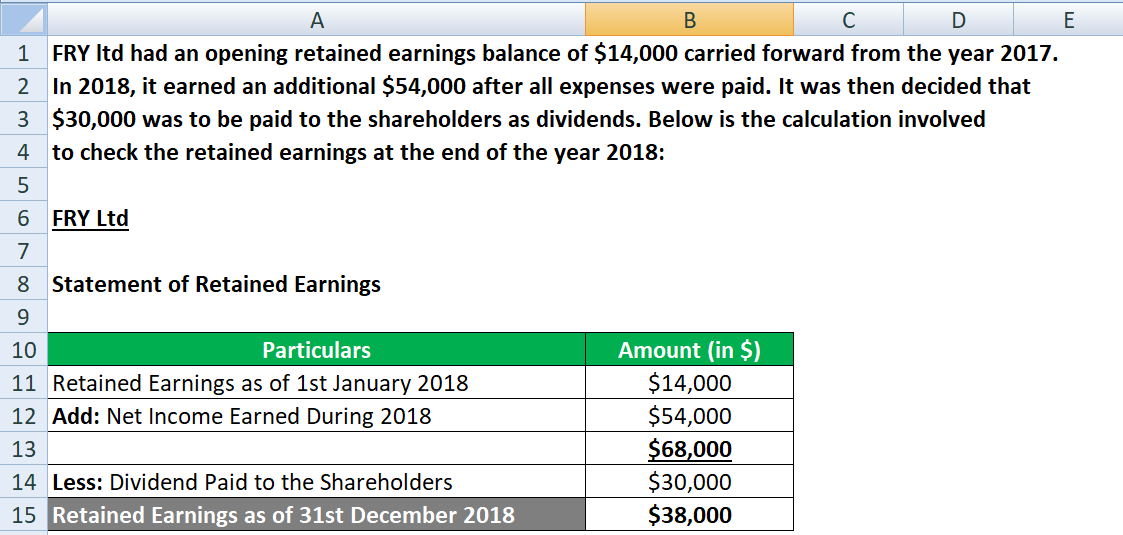
To calculate Retained Earnings, the beginning Retained Earnings balance is added to the net income or loss and then dividend payouts are subtracted. Net income is like the heartbeat of your company’s financial health, pulsating through the veins of your statement of retained earnings. Think of it as the hard-earned result of your business operations—the grand total after expenses bow out of revenues’ spotlight. The statement of retained earnings (retained earnings statement) is a financial statement that outlines the changes in retained earnings for a company over a specified period. This statement reconciles the beginning and ending retained earnings for the period, using information such as net income from the other financial statements.
- Remember, you might have a mountain of retained earnings and still run into daily cash flow issues if that money is tied up elsewhere.
- Hence, the technology company will likely have higher retained earnings than the T-shirt manufacturer.
- Net income is the amount of money a company has after subtracting revenue costs.
- A company that doesn’t pay dividends could multiply an investor’s capital, provided things go well.
- It’s often an alert to investors and managers to review the company’s financial health and strategies.
Step 3 of 3
It demonstrates a balanced approach to managing earnings that can be conducive to sustainable growth. With our stage set and our actors—beginning balance, net income, and dividends—in the limelight, the scene is ready for a demonstration of the retained earnings calculation in action. Your company could decide to reinvest the earnings back into the business instead.
Appropriated retained earnings are those set aside for specific purposes, such as funding capital expenditures or paying off debt. For example, even if you retain earnings to invest in a major marketing campaign, you need enough cash on hand to execute your plan. This means the company was able to generate $5 in market value for each dollar of earnings it retained. Had the company used debt capital instead, they’d have generated less value because of the interest payment; internally generated capital helps profitable companies create value more efficiently. The statement of retained earnings is primarily used to assess the management’s future outlook for the business. For example, any common stock you buy back during the year should be deducted from the earnings.
In studying “Financial Statement Modeling” for the CFA, you should learn to construct and analyze financial models that integrate income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Understand the forecasting techniques for projecting revenues, expenses, capital expenditures, and working capital requirements. Analyze how assumptions on growth rates, margins, and key financial ratios impact a company’s financial outlook and valuation.
It’s a measure of the company’s total profit that’s been reinvested back into the business, rather than paid out to shareholders. This step is a testament to the financial decisions made over the period. You’ve gathered your beginning balance, tallied up the profits or weathered the losses, and decided regarding dividends.