Biodiesel Price Trend and Market Analysis
Biodiesel, an alternative fuel derived from renewable resources, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its environmental benefits and potential to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. The price of biodiesel is influenced by various factors, including feedstock costs, production processes, demand and supply dynamics, and global economic conditions. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the recent biodiesel price trend, examining the key drivers, market dynamics, and future outlook.
Introduction to Biodiesel
Biodiesel is a renewable fuel made from a variety of sources, including vegetable oils, animal fats, and recycled cooking oils. It can be used in its pure form (B100) or blended with petroleum diesel in various proportions (e.g., B20, which is 20% biodiesel and 80% petroleum diesel). Key benefits of biodiesel include:
Environmental Impact: Biodiesel reduces greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants compared to conventional diesel.Energy Security: Biodiesel can help reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels.Biodegradability: Biodiesel is non-toxic and biodegradable, making it safer for the environment.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/biodiesel-price-trends/pricerequest
Biodiesel is a renewable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional diesel fuel, derived from vegetable oils, animal fats, and recycled cooking oils. As the world seeks to reduce its carbon footprint and dependence on fossil fuels, biodiesel has gained significant attention. Understanding the price trends of biodiesel is essential for producers, suppliers, and end-users to make informed decisions. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of biodiesel prices, examining the factors influencing these trends, regional variations, and future market forecasts.
Market Overview
Biodiesel production involves the transesterification of fats and oils with methanol or ethanol in the presence of a catalyst, producing glycerin as a byproduct. The global market for biodiesel is influenced by several factors, including raw material costs, energy costs, production capacities, demand from various sectors, and government policies.
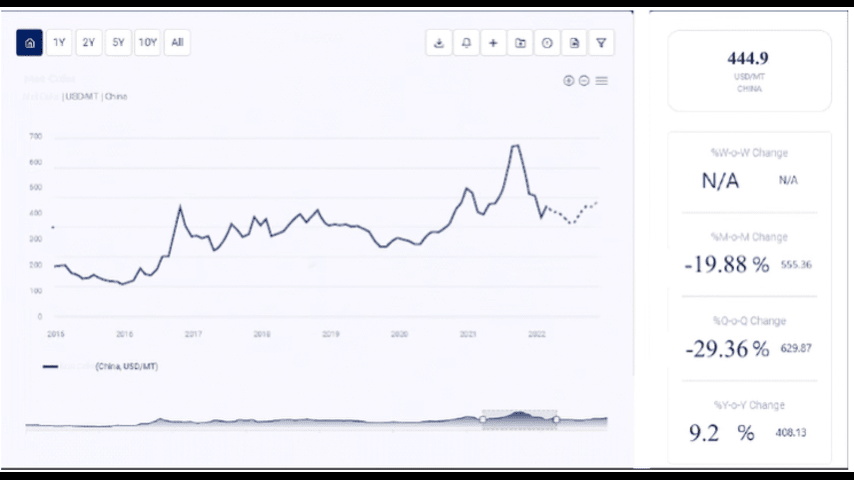
Current Biodiesel Price Trends
As of mid-2024, the price of biodiesel has shown variability due to various market dynamics. The average global price of biodiesel ranges between $1.00 and $1.50 per liter. Several key factors contribute to these price trends:
- Raw Material Costs: The primary raw materials for producing biodiesel are vegetable oils (such as soybean, palm, and canola oil), animal fats, and recycled cooking oils. Fluctuations in the prices of these materials, driven by factors such as agricultural yields, supply chain disruptions, and global demand, directly impact production costs.
- Energy Costs: The production of biodiesel is energy-intensive, requiring significant amounts of electricity and heat for the transesterification and purification processes. Energy costs can vary based on local energy prices and the efficiency of the production process.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: The balance between supply and demand plays a crucial role in determining prices. High demand from the transportation and industrial sectors, coupled with limited supply, can drive prices up, while an oversupply can lead to price reductions.
- Production Capacities: The global production capacity for biodiesel affects its market price. Expansions in production facilities or the establishment of new plants can lead to a surplus in supply, thereby reducing prices. Conversely, production disruptions can lead to shortages and price hikes.
- Government Policies: Policies, including subsidies, mandates, and tax incentives, can significantly affect the price of biodiesel. Changes in government regulations or incentives can either support or hinder the biodiesel market.
Conclusion
Businesses involved in the production, distribution, or utilization of biodiesel should closely monitor these trends to make informed decisions and optimize their operations.
In summary, while the biodiesel market faces several challenges and uncertainties, it also presents opportunities for growth and innovation. By understanding the key factors influencing prices and staying abreast of market developments, businesses can navigate the dynamic landscape and achieve long-term success.