Understanding Prostate Cancer and the Role of a Urologist
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer affecting men globally. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are critical to managing this condition, and a urologist plays a pivotal role in the process. In this article, we explore prostate cancer, its symptoms, diagnosis, and how urologists contribute to patient care and recovery.
What is Prostate Cancer?
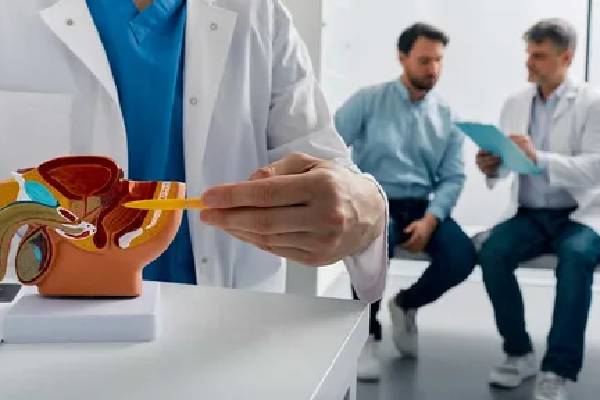
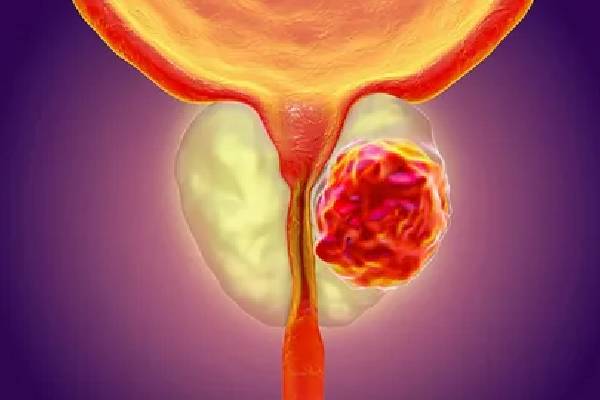
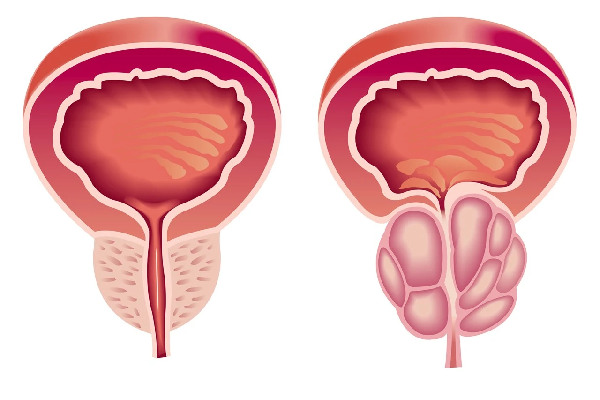
Prostate cancer originates in the prostate gland, a small, walnut-shaped organ in the male reproductive system. The prostate produces seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. While many prostate cancers grow slowly, some types can be aggressive and spread quickly.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
In its early stages, prostate cancer may not show noticeable symptoms. However, as it progresses, common signs include:
- Difficulty urinating or a weak urine stream
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area
- Bone pain (in advanced cases)
- Erectile dysfunction
Early detection is crucial, as advanced prostate cancer is harder to treat.
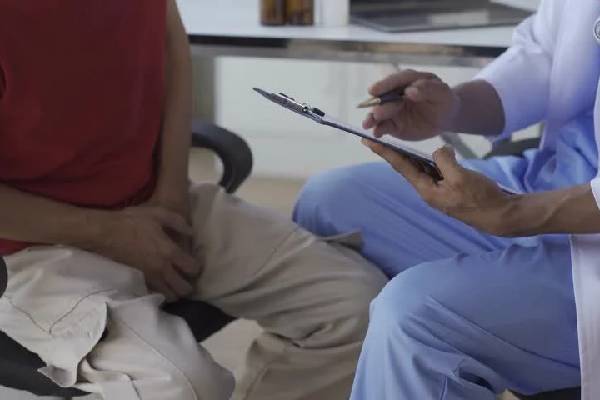
The Role of a Urologist
A urologist specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases of the urinary tract and male reproductive organs. For prostate cancer, their expertise is indispensable throughout the journey of diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care.
Key Responsibilities of a Urologist in Prostate Cancer
- Screening and Diagnosis
- Conducting PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) blood tests to detect elevated protein levels linked to prostate cancer.
- Performing digital rectal exams (DRE) to feel for abnormalities in the prostate gland.
- Ordering imaging tests like MRIs or biopsies for confirmation.
- Developing a Treatment Plan
- Advising patients on treatment options based on cancer stage and overall health.
- Coordinating care with oncologists for advanced cases requiring chemotherapy or radiation.
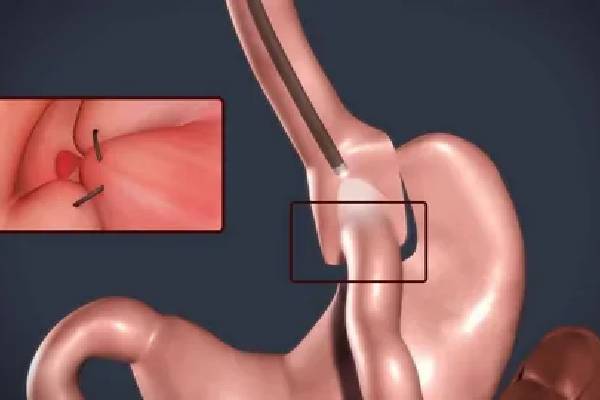
- Performing Surgical Procedures
- Conducting prostatectomy (surgical removal of the prostate) for localized cancer.
- Utilizing minimally invasive techniques like robotic-assisted surgery for precision.
- Providing Long-Term Follow-Up
- Monitoring PSA levels post-treatment to ensure cancer does not return.
- Addressing complications like urinary incontinence or erectile dysfunction.
Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
Steps to Diagnosis
- Screening Tests
- PSA blood test and DRE are initial steps in detecting abnormalities.
- Imaging Techniques
- MRI or CT scans provide detailed visuals of the prostate and surrounding tissues.
- Biopsy
- A small tissue sample from the prostate is examined under a microscope to confirm cancer.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
Active Surveillance
- Suitable for early-stage, slow-growing cancer.
- Involves regular monitoring without immediate treatment.
Surgery
- Radical prostatectomy removes the prostate gland and nearby tissues.
- Robotic-assisted surgery ensures precision and faster recovery.
Radiation Therapy
- Uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
Hormone Therapy
- Reduces testosterone levels to slow cancer growth.
Chemotherapy
- Recommended for advanced stages where cancer has spread.
Choosing the Right Urologist
Selecting a skilled and experienced urologist can significantly impact your treatment outcome. Factors to consider include:
- Credentials: Board certification in urology.
- Experience: Specialization in prostate cancer treatment.
- Communication: Ability to explain complex procedures clearly.
- Hospital Affiliation: Access to advanced facilities and technologies.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Tips
Although the exact cause of prostate cancer remains unknown, adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce risk factors:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly to improve overall health.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Discuss genetic testing with your doctor if you have a family history of prostate cancer.
Conclusion
A urologist is a vital partner in the fight against prostate cancer, offering expertise in early detection, treatment, and management. Timely consultations and proactive health measures can make a significant difference in outcomes. If you or a loved one is at risk, schedule regular screenings and seek the guidance of a trusted urologist to stay ahead of the condition.
By staying informed and vigilant, you can navigate prostate cancer with confidence and care.