Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a crucial component in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and cosmetics. The Vitamin C price trend analysis have been influenced by multiple factors such as supply chain disruptions, raw material costs, and changing demand patterns. This article provides an in-depth analysis of Vitamin C price trends, key influencing factors, and forecasts for 2024.
Raw Material Costs
The primary raw material for Vitamin C production is corn, which is processed to produce glucose. This glucose is then converted into ascorbic acid through a complex chemical process involving several intermediates. Fluctuations in corn prices directly impact the cost of producing Vitamin C. Factors such as weather conditions, agricultural policies, and global trade dynamics can cause significant variations in corn prices, thereby affecting the overall production cost of Vitamin C.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/vitamin-c-price-trends/pricerequest
Production Processes
Vitamin C production is primarily carried out using two methods: the Reichstein process and the two-step fermentation process.
- Reichstein Process: This is a classical method involving the conversion of glucose to sorbitol, followed by fermentation to produce ascorbic acid. This process, though effective, is energy-intensive and has high operational costs due to the need for multiple chemical steps and stringent purification processes.
- Two-Step Fermentation Process: This more modern approach involves biotechnological fermentation of glucose using genetically modified microorganisms. This method is generally more cost-effective and environmentally friendly, reducing the overall production cost of Vitamin C. However, any changes in the biotechnology market or regulatory issues surrounding GMOs can influence the cost structure.
Global Demand
Vitamin C is in constant demand across various sectors:
- Dietary Supplements: The increasing awareness of health and wellness has led to a surge in the consumption of Vitamin C supplements. The COVID-19 pandemic significantly boosted this demand as Vitamin C was touted for its immune-boosting properties.
- Pharmaceuticals: Vitamin C is used in various pharmaceutical formulations, driving steady demand in this sector.
- Cosmetics: With its antioxidant properties, Vitamin C is a popular ingredient in skincare products, further contributing to its demand.
Supply Chain Logistics
The global supply chain for Vitamin C is complex and involves several key players, including raw material suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. Any disruptions in the supply chain, such as those caused by geopolitical tensions, trade restrictions, or logistical challenges, can impact the availability and price of Vitamin C. For instance, the pandemic caused significant disruptions, leading to price volatility due to supply shortages and increased transportation costs.
Regional Factors
The production and pricing of Vitamin C can vary significantly across different regions:
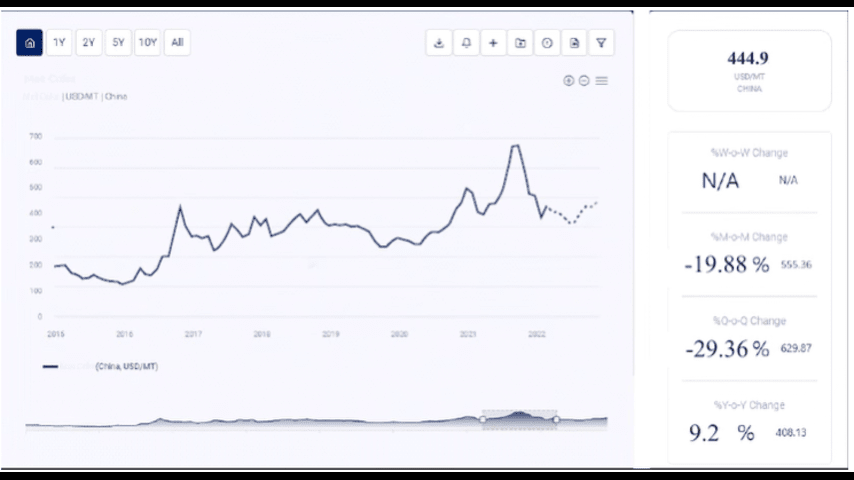
- China: As the largest producer of Vitamin C, China plays a pivotal role in the global market. Factors such as environmental regulations, labor costs, and government policies in China can have a substantial impact on global Vitamin C prices.
- Europe: European production is influenced by stringent environmental regulations and higher operational costs. However, the demand for high-quality and sustainable production methods can justify higher prices in this region.
- North America: The North American market benefits from advanced production technologies and efficient supply chains, but higher labor and regulatory costs can affect the pricing structure.
Technological Innovations
Advancements in production technologies can significantly impact the cost and efficiency of Vitamin C production. Innovations in fermentation technology, process optimization, and waste reduction can lead to cost savings and more stable pricing. Additionally, research into alternative raw materials and production methods can offer new avenues for cost-effective Vitamin C production.
Environmental and Regulatory Factors
Environmental regulations aimed at reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainable practices can influence the production cost of Vitamin C. Compliance with these regulations often requires investment in cleaner technologies and processes, which can increase production costs but also lead to long-term benefits through enhanced sustainability and market preference for environmentally friendly products.
Conclusion
The price trend of Vitamin C is shaped by a complex interplay of raw material costs, production methods, global demand, supply chain logistics, and regional factors. Understanding these elements is crucial for stakeholders in the Vitamin C market to navigate price fluctuations effectively. As technological advancements and sustainability initiatives continue to evolve, the future of Vitamin C pricing will be influenced by the ability to balance cost efficiency, environmental responsibility, and market demand.
By staying informed about these trends and developments, manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers can make strategic decisions to optimize their roles in the Vitamin C supply chain.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *